IVF
(IN-VITRO FERTILIZATION)
What Is In-vitro Fertilization?
This treatment requires hormonal stimulation in order to obtain eggs, which once fertilized in the laboratory will be implanted in the uterus to achieve pregnancy. The purpose of this process is to obtain quality embryos with which to increase the chances of achieving pregnancy.
This procedure increases the chances of pregnancy with respect to sexual intercourse for several reasons. It includes a process of ovarian stimulation, which seeks the development of several ovarian follicles through a pattern of stimulation with gonadotropins. In this way, the growth and maturation of the follicles is controlled, which increases the chances of pregnancy by having more than one egg that can be fertilized and developed into a viable embryo.
The semen sample is processed in the laboratory in order to select the highest quality sperm. Embryos are cultured in the laboratory under constant supervision and control to select the embryo with the greatest implantation potential. The procedure is scheduled to take place at the optimal time, relative to the preparation of the endometrium.
Step by step approach for IVF treatment
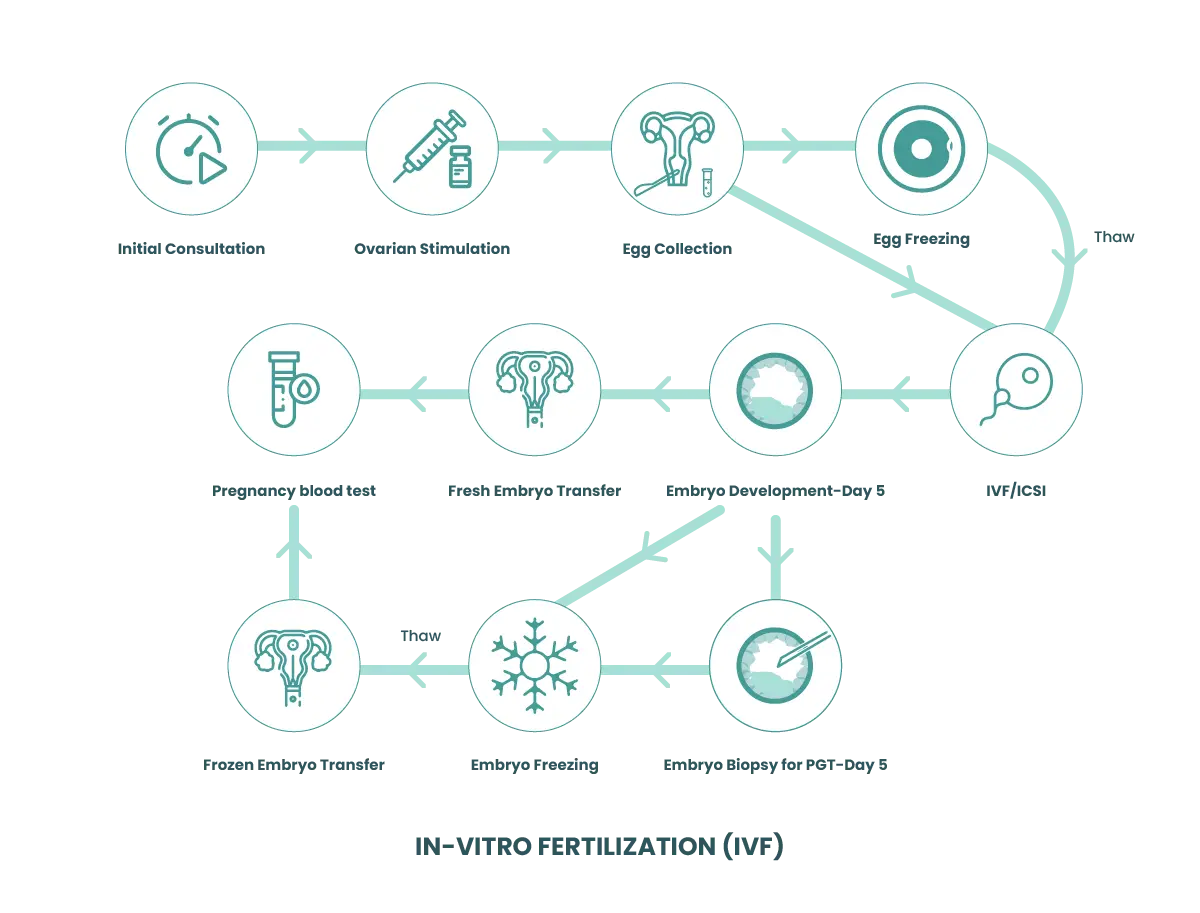
Step 01: Ovarian Stimulation
With the start of treatment, which is marked by the woman’s menstrual cycle, ovarian stimulation begins, which has an estimated duration of 10-12 days. This stimulation increases the chances of success, since the woman naturally only produces one ovum in each menstrual cycle, while in this way the development of more than one follicle is ensured.
Step 02: follicular Preparation / Control
The specialist performs an exhaustive follow-up of the stimulation, controlling the development of the cycle through ultrasound, until verifying that the number and size of the follicles are adequate.
Step 03: Puncture
It consists of the aspiration of the follicles to extract the eggs while the patient is under sedation. When the oocytes are mature and have reached their optimum moment, we retrieve them by aspiration through needle-guided vaginal ultrasound. It is a simple procedure that does not last more than 15-20 minutes and is performed in the operating room under sedation to avoid any possible discomfort to the patient.
Step 04: In-vitro fertilization
It consists of contacting, in the laboratory, the ovules with the processed semen sample of the couple. There are two ways to carry out this process:
- Conventional IVF: This consists of depositing each of the ovules obtained in the puncture in drops of previously prepared semen to stimulate the natural fertilization process in the culture dish.
- ICSI: This consists of the introduction of a selected spermatozoon inside a mature egg to achieve fertilization.
Step 05: Embryo Culture
The culture of the embryos lasts between 5 to 6 days. After fertilization, the embryos begin their development in incubators with a culture medium that provides them with what is necessary for their growth. During this time, embryologists observe and analyze the development of embryos in order to assess their quality.
Step 06: Embryo Transfer
The patient’s uterus is prepared to ensure that the endometrium has the optimal thickness to receive the embryo and facilitate pregnancy. Subsequently, the best embryo is transferred to the uterus through a simple intervention vaginally, and this process does not require anesthesia.
Step 07: Pregnancy Test / Gestational Follow-up
If the pregnancy test is positive, 6 weeks later, a control ultrasound is performed in which the embryo sac is confirmed.
